| > |
 |
This system of differential equations (DE1) has two eigenvalues of opposite sign (λ=1 and λ=−2). The point (0,0) is unstable and called a saddle point.
| > |
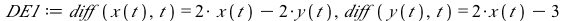
 |
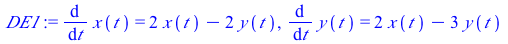 |
(1) |
| > |
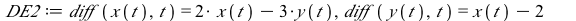
 |
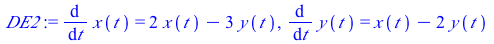 |
(2) |
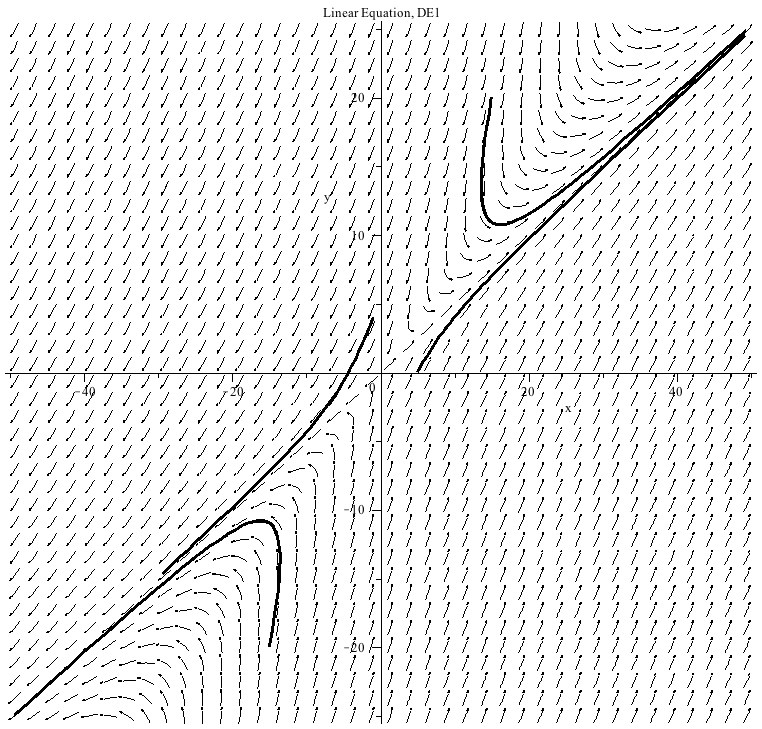
This system of differential equations (DE2) has two eigenvalues of opposite sign (λ=1 and λ=−1). The point (0,0) is unstable and called a saddle point.
| > |
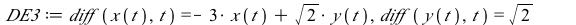
 |
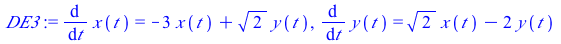 |
(3) |
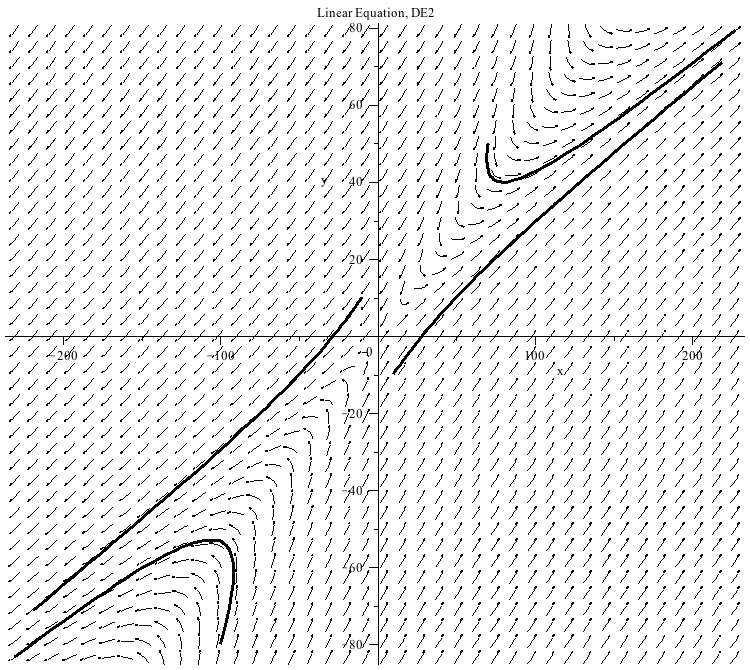
This system of differential equations (DE3) has two negative eigenvalues (λ=−1 and λ=−4). The point (0,0) is called a sink or a stable node.
| > |
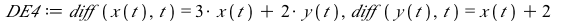
 |
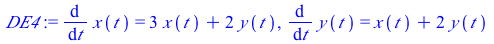 |
(4) |
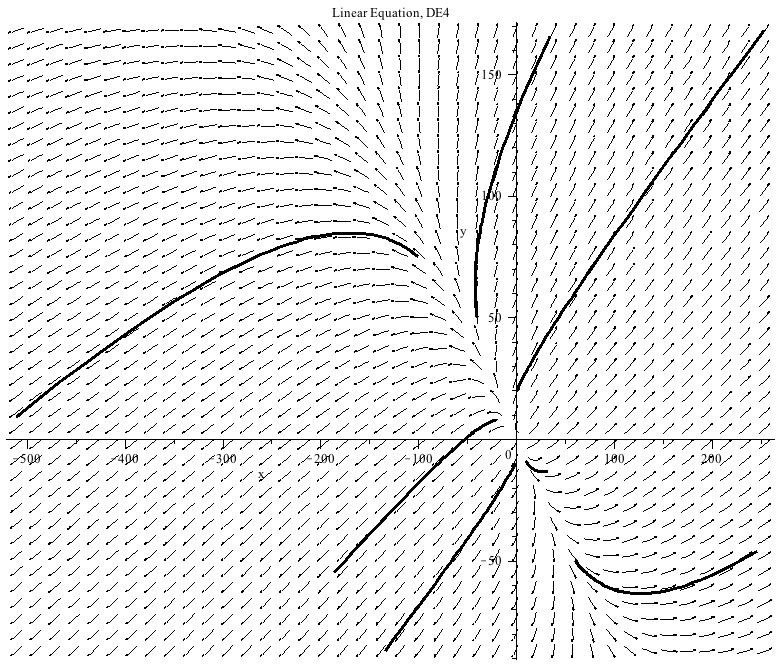
This system of differential equations (DE4) has two positive eigenvalues (λ=1 and λ=4). The point (0,0) is called a source or an unstable node.
| > |
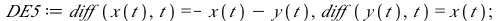 |
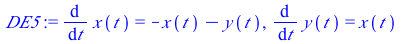 |
(5) |
This system of differential equations (DE5) has two complex conjugate eigenvalues (λ=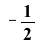 ±
±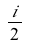
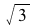 ) with a negative real part. The point (0,0) is called a stable spiral.
) with a negative real part. The point (0,0) is called a stable spiral.
| > |
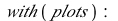 |
| > |
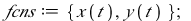 |
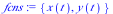 |
(6) |
| > |
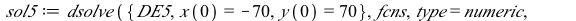
 |
 |
(7) |
| > |
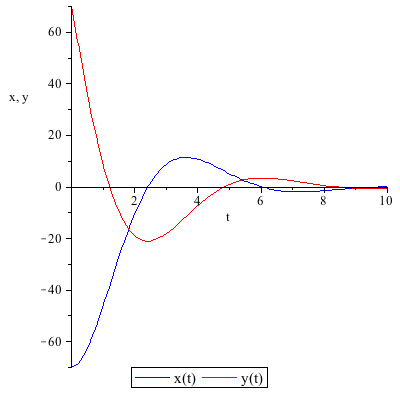
![odeplot(sol5, [[t, x(t)], [t, y(t)]], 0 .. 10, color = [](images/worksheet_lin_diff_eq_52.gif)
![odeplot(sol5, [[t, x(t)], [t, y(t)]], 0 .. 10, color = [](images/worksheet_lin_diff_eq_53.gif) |
| > |
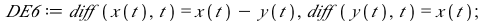 |
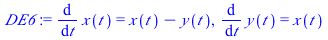 |
(8) |
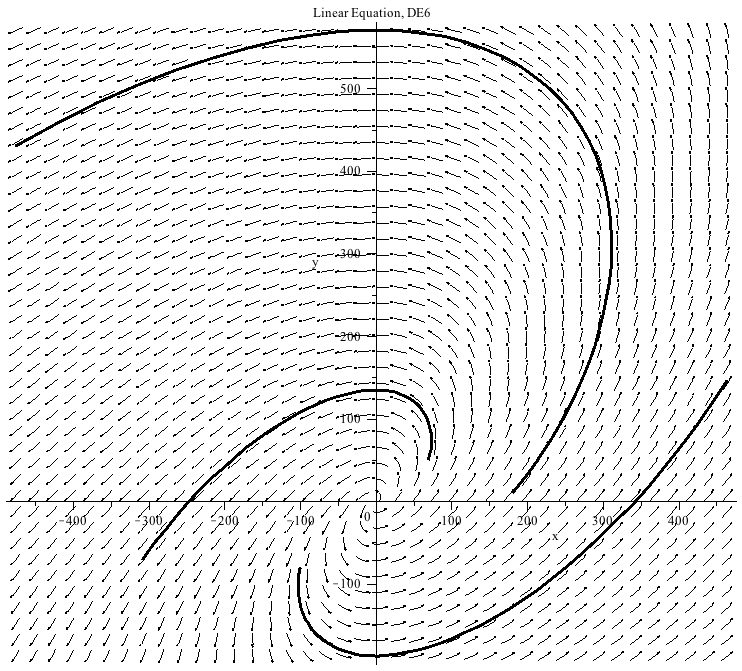
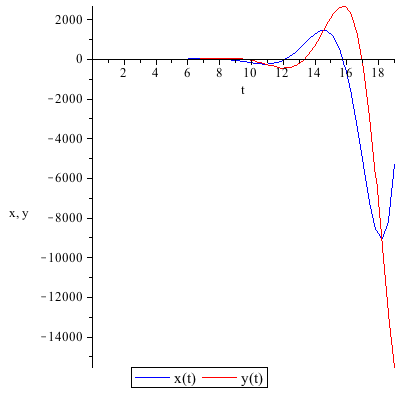
This system of differential equations (DE6) has two complex conjugate eigenvalues (λ=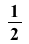 ±
±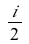
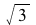 ) with a positive real part. The point (0,0) is called an unstable spiral.
) with a positive real part. The point (0,0) is called an unstable spiral.
| > |
 |
| > |
 |
 |
(9) |
| > |
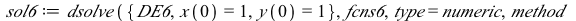
 |
 |
(10) |
| > |
![odeplot(sol6, [[t, x(t)], [t, y(t)]], 0 .. 19, color = [](images/worksheet_lin_diff_eq_71.gif)
![odeplot(sol6, [[t, x(t)], [t, y(t)]], 0 .. 19, color = [](images/worksheet_lin_diff_eq_72.gif) |
![]() ±
±![]()
![]() ) with a negative real part. The point (0,0) is called a stable spiral.
) with a negative real part. The point (0,0) is called a stable spiral. 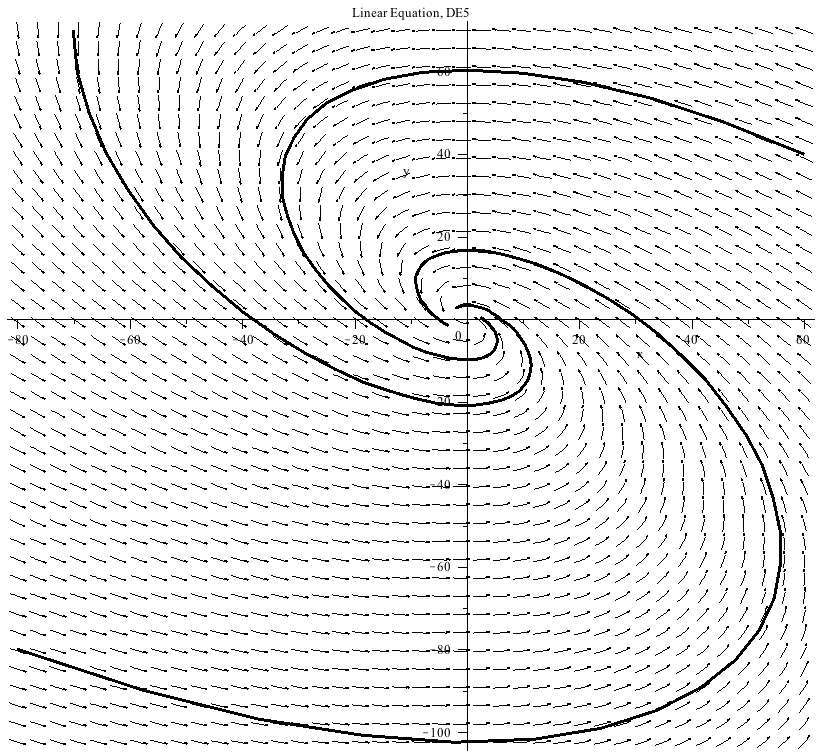
![]() ±
±![]()
![]() ) with a positive real part. The point (0,0) is called an unstable spiral.
) with a positive real part. The point (0,0) is called an unstable spiral.