Exercises 2.6 Practice Problems
Exercise Group.
For each of the following functions, evaluate at the given input.
\(\displaystyle f(3)\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)\)
\(\displaystyle f(-1)\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)\)
1.
\(f(x)=3-8x\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=-21\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)=-29\)
\(\displaystyle f(-1)=11\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)=-3\)
2.
\(f(x)=6x-4\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=14\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)=20\)
\(\displaystyle f(-1)=-10\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
3.
\(f(x)=26\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=26\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)=26\)
\(\displaystyle f(-1)=26\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)=26\)
4.
\(f(x)=-x+6\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=3\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)=2\)
\(\displaystyle f(-1)=7\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)=5 \frac{1}{4} \)
5.
\(f(x)=2x\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=6\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)=8\)
\(\displaystyle f(-1)=-2\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)= \frac{3}{2}\)
6.
\(f(x)=-\left(\frac{2}{3}\right)x + 1\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=-1\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)=-\frac{5}{3}\)
\(\displaystyle f(-1)=\frac{5}{3}\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)=\frac{1}{2} \)
Exercise Group.
For each of the following functions, evaluate at the given input.
\(\displaystyle g(c)\)
\(\displaystyle g(2e)\)
\(\displaystyle g(-k)\)
\(\displaystyle g\left(\frac{1}{2}h\right)\)
7.
\(g(x)=2-4x\)
\(\displaystyle g(c)=2-4c\)
\(\displaystyle g(2e)=2-8e\)
\(\displaystyle g(-k)=2+4k\)
\(\displaystyle g\left(\frac{1}{2}h\right)=2-2h\)
8.
\(f(x)=3x-3\)
\(\displaystyle g(c)=3c-3\)
\(\displaystyle g(2e)=6e-3\)
\(\displaystyle g(-k)=-3k-3\)
\(\displaystyle g\left(\frac{1}{2}h\right)=\frac{3}{2}h-3\)
9.
\(g(x)=12\)
\(\displaystyle g(c)=12\)
\(\displaystyle g(2e)=12\)
\(\displaystyle g(-k)=12\)
\(\displaystyle g\left(\frac{1}{2}h\right)=12\)
10.
\(g(x)=x-1\)
\(\displaystyle g(c)=c-1\)
\(\displaystyle g(2e)=2e-1\)
\(\displaystyle g(-k)=-k-1\)
\(\displaystyle g\left(\frac{1}{2}h\right)=\frac{1}{2}h-1\)
11.
\(g(x)=x\)
\(\displaystyle g(c)=c\)
\(\displaystyle g(2e)=2e\)
\(\displaystyle g(-k)=-k\)
\(\displaystyle g\left(\frac{1}{2}h\right)=\frac{1}{2}h\)
12.
\(g(x)=-\frac{1}{4}x + 2\)
\(\displaystyle g(c)=-\frac{1}{4}c+2\)
\(\displaystyle g(2e)=-\frac{1}{2}e+2\)
\(\displaystyle g(-k)=\frac{1}{4}k+2\)
\(\displaystyle g\left(\frac{1}{2}h\right)=\frac{1}{8}h+2\)
Exercise Group.
For each of the following functions, evaluate the given input.
\(\displaystyle f(x) = 2x+3\)
\(\displaystyle g(x) = 10x\)
\(\displaystyle h(x) = 0\)
\(\displaystyle y(x) = \frac{1}{5}x\)
13.
Evaluate all four of the above functions given \(x=1 \text{.}\)
\(\displaystyle f(1)=5\)
\(\displaystyle g(1)=10\)
\(\displaystyle h(1)=0\)
\(\displaystyle y(1)=\frac{1}{5}\)
14.
Evaluate all four of the above functions given \(x=a \text{.}\)
\(\displaystyle f(a)=2a+3\)
\(\displaystyle g(a)=10a\)
\(\displaystyle h(a)=0\)
\(\displaystyle y(a)=\frac{1}{5}a\)
15.
Evaluate all four of the above functions given \(x=0 \text{.}\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)=3\)
\(\displaystyle g(0)=0\)
\(\displaystyle h(0)=0\)
\(\displaystyle y(0)=0\)
16.
Evaluate all four of the above functions given \(x=2z \text{.}\)
\(\displaystyle f(2z)=4z+3\)
\(\displaystyle g(2z)=20z\)
\(\displaystyle h(2z)=0\)
\(\displaystyle y(2z)=\frac{2}{5}z\)
17.
Evaluate all four of the above functions given \(x=\frac{1}{2} \text{.}\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=4\)
\(\displaystyle g\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=5\)
\(\displaystyle h\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=0\)
\(\displaystyle y\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=\frac{1}{10}\)
18.
Evaluate all four of the above functions given \(x=b+5 \text{.}\)
\(\displaystyle f(b+5)=2b+13\)
\(\displaystyle g(b+5)=10b + 50\)
\(\displaystyle h(b+5)=0\)
\(\displaystyle y(b+5)=\frac{1}{5}b + 1\)
19.
Suppose \(a(t)= \frac{1}{19}\text{.}\)
Evaluate \(a(1)\text{.}\)
Evaluate \(a(b+c)\text{.}\)
Evaluate \(a(9)\text{.}\)
Evaluate \(a(\frac{1}{19})\text{.}\)
\(\displaystyle a(1) = \frac{1}{19}\)
\(\displaystyle a(b+c)) = \frac{1}{19}\)
\(\displaystyle a(9) = \frac{1}{19}\)
\(\displaystyle a\left(\frac{1}{19}\right) = \frac{1}{19}\)
20.
Suppose \(d(t)=\pi t\text{.}\)
Evaluate \(d(0)\text{.}\)
Evaluate \(d(a+h)\text{.}\)
Evaluate \(d(x)\text{.}\)
Evaluate \(d(\sqrt{x+3})\text{.}\)
\(\displaystyle d(0) = 0\)
\(\displaystyle d(a+h) = \pi a + \pi h\)
\(\displaystyle d(x) = \pi x\)
\(\displaystyle d(\sqrt{x+3}) = \left( \pi \right) \left( \sqrt{x+3} \right)\)
21.
Suppose
We want to evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle g(0)\)
\(\displaystyle g(-5)\)
\(\displaystyle g(10)\)
\(\displaystyle g(2)\)
\(\displaystyle g(0)=0\)
\(\displaystyle g(-5)= -2\)
\(\displaystyle g(10)= \sqrt{10}\)
\(\displaystyle g(2) = 4\)
22.
Suppose
We want to evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle h(1)\)
\(\displaystyle h(3)\)
\(\displaystyle h(0)\)
\(\displaystyle h(-3)\)
\(\displaystyle h(1) = 1\)
\(\displaystyle h(3) = \frac{3}{2}\)
\(\displaystyle h(0) = 3\)
\(\displaystyle h(-3) = 0\)
23.
Suppose
We want to evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle f(1)\)
\(\displaystyle f(5)\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle f(1) = 1\)
\(\displaystyle f(5) = \frac{5}{3}\)
\(\displaystyle f(0) = 0\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{3}{2}\right) = \sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}\)
24.
Suppose
We want to evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle f(-1)\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)\)
\(\displaystyle f(2)\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle f(-1) = 1\)
\(\displaystyle f(0) = 0\)
\(\displaystyle f(2) = \frac{1}{2}\)
\(\displaystyle f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right) = 2\)
25.
Suppose
We want to evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle f(-10)\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)\)
\(\displaystyle f(10)\)
\(\displaystyle f(20)\)
\(\displaystyle f(-10)=-1\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)=-1\)
\(\displaystyle f(10)=20\)
\(\displaystyle f(20)=\frac{1}{2}\)
26.
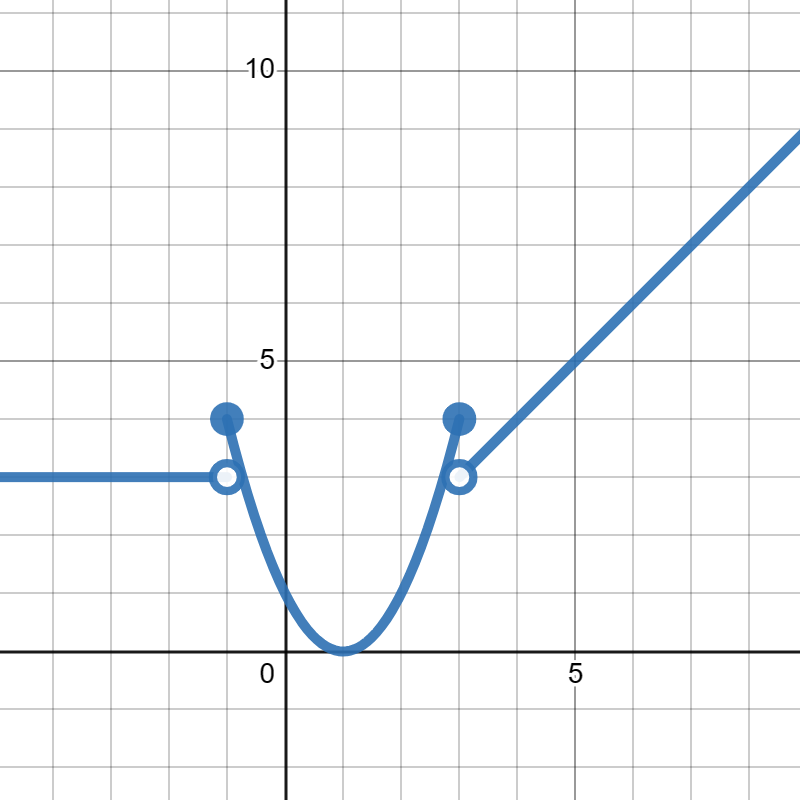
Suppose \(g(x)\) is given in the graph below:
Evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle g(-2)\)
\(\displaystyle g(4)\)
\(\displaystyle g(6)\)
\(\displaystyle g(8)\)
\(\displaystyle g(9)\)
\(\displaystyle g(-2)=-1\)
\(\displaystyle g(4)=3\)
\(\displaystyle g(6)=5\)
\(\displaystyle g(8)=11\)
\(\displaystyle g(9)=12\)
27.
Suppose \(f(x)\) is given in the graph below:
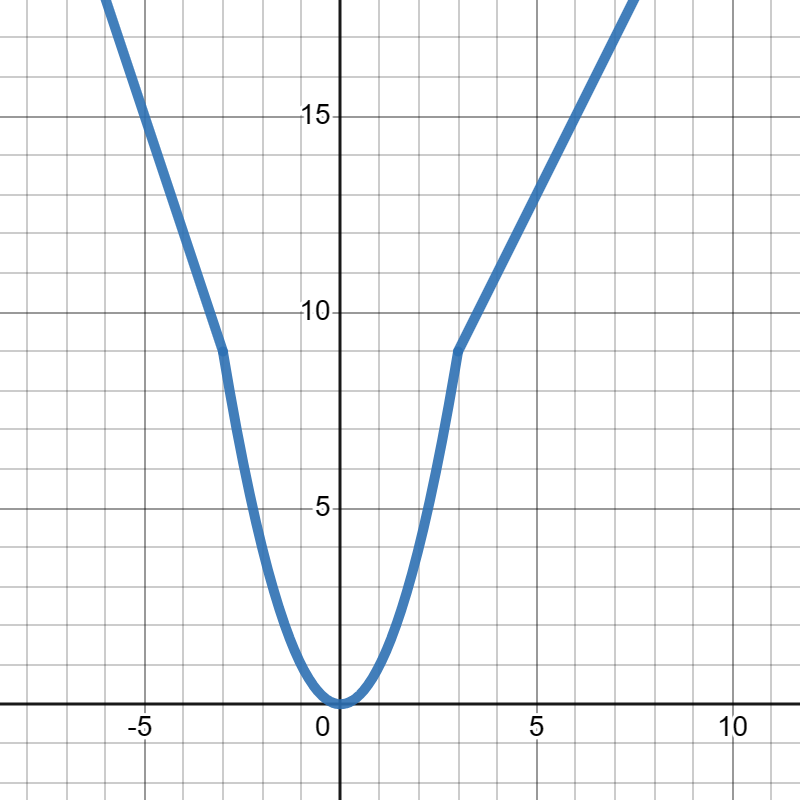
Evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle f(-3)\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)\)
\(\displaystyle f(5)\)
\(\displaystyle f(7)\)
\(\displaystyle f(-3)=9\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)=0\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=9\)
\(\displaystyle f(5)=13\)
\(\displaystyle f(7)=17\)
28.
Suppose \(f(x)\) is given in the table below:
| \(x\) | \(f(x)\) |
| \(-3\) | \(1\) |
| \(0\) | \(2\) |
| \(3\) | \(-7\) |
| \(6\) | \(/pi\) |
| \(\frac{1}{3}\) | \(4.31\) |
Evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle f(-3)\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)\)
\(\displaystyle f(6)\)
\(\displaystyle f(\frac{1}{3})\)
\(\displaystyle f(-3)=1\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)=2\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=-7\)
\(\displaystyle f(6)=\pi\)
\(\displaystyle f(\frac{1}{3})=4.31\)
29.
Suppose \(f(t)\) is given in the table below:
| \(t\) | \(f(t)\) |
| \(0\) | \(1\) |
| \(1\) | \(2\) |
| \(2\) | \(3\) |
| \(3\) | \(4\) |
| \(4\) | \(5\) |
Evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle f(0)\)
\(\displaystyle f(1)\)
\(\displaystyle f(2)\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)\)
\(\displaystyle f(0)=1\)
\(\displaystyle f(1)=2\)
\(\displaystyle f(2)=3\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=4\)
\(\displaystyle f(4)=5\)
30.
Suppose \(f(x)\text{,}\) \(g(x)\text{,}\) and \(h(x)\) are given in the table below:
| x | f(x) | g(x) | h(x) |
| 0 | 9 | 4 | 1 |
| 1 | -2 | 5.5 | -3 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 3 | 7 | 0 | 8 |
| 4 | -1 | 8 | -4 |
Evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle h(0)\)
\(\displaystyle f(1)\)
\(\displaystyle g(2)\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)\)
\(\displaystyle h(4)\)
\(\displaystyle h(0)=1\)
\(\displaystyle f(1)=-2\)
\(\displaystyle g(2)=6\)
\(\displaystyle f(3)=7\)
\(\displaystyle h(4)=-4\)
31.
Suppose \(m(x)\) is given in the table below:
| x | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| m(x) | 6 | 2 | -1 | -5 | -8 |
Evaluate each of the following:
\(\displaystyle m(5)\)
\(\displaystyle m(1)\)
\(\displaystyle m(9)\)
\(\displaystyle m(3)\)
\(\displaystyle m(7)\)
\(\displaystyle m(5)=-1\)
\(\displaystyle m(1)=6\)
\(\displaystyle m(9)=-8\)
\(\displaystyle m(3)=2\)
\(\displaystyle m(7)=-5\)
Exercise Group.
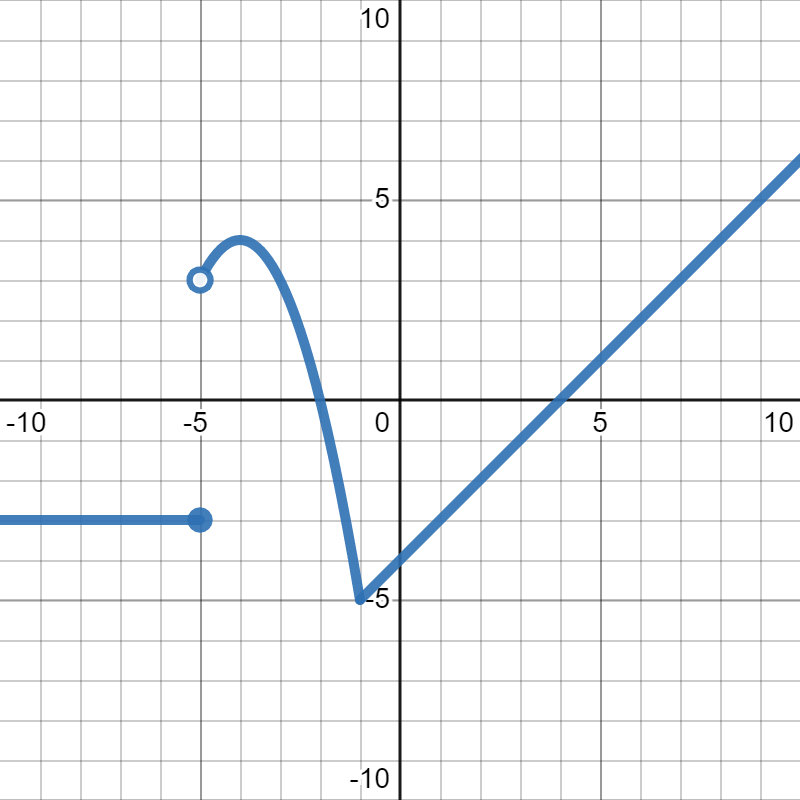
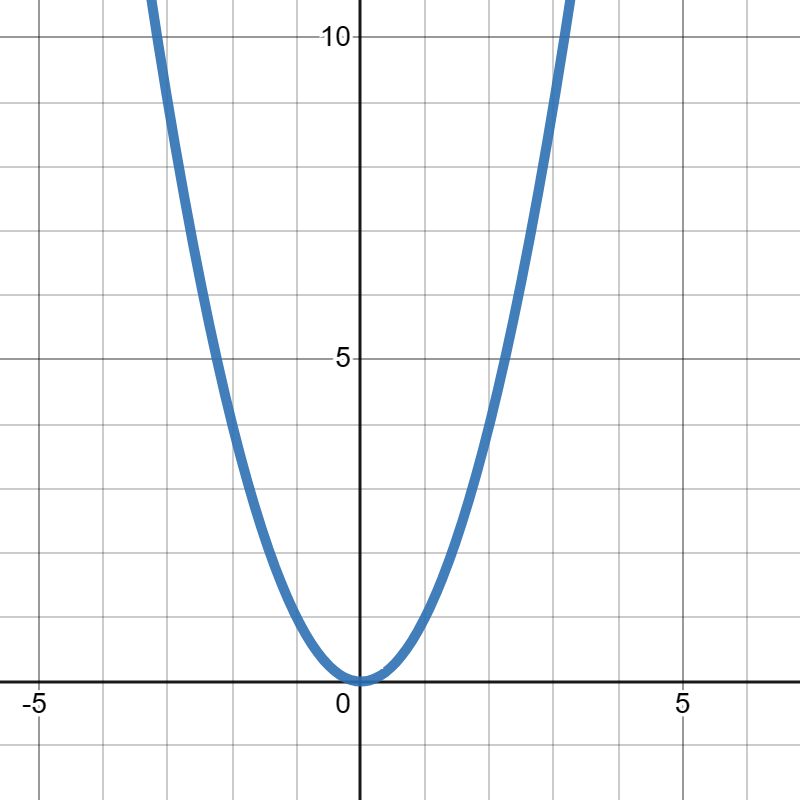
Suppose \(f(x)= 3x-3\) and \(g(x)\) is given in the graph below:
32.
Evaluate \(2f(2)-g(0)+1\text{.}\)
\(2f(2)-g(0)+1=7\)
33.
Evaluate \(g(2)-(g(-2))^2\text{.}\)
\(g(2)-(g(-2))^2=-12\)
34.
Evaluate \(5g(-1)+4f(3)\text{.}\)
\(5g(-1)+4f(3)=-29\)
35.
Evaluate \(\frac{1}{2}f(5)-2f(0)\text{.}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}f(5)-2f(0)=0\)
36.
Evaluate \((f(-2))^2-f(0)-(g(2))^3\text{.}\)
\((f(-2))^2-f(0)-(g(2))^3=20\)
Exercise Group.
Suppose \(f(x)= x\) and \(g(x)\) is given in the table below:
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| g(x) | 6 | 4 | -1 | 7 | 0 |
37.
Evaluate \(2f(2)-g(1)+1\text{.}\)
\(2f(2)-g(1)+1=-1\)
38.
Evaluate \(g(4)-(g(3))^3\text{.}\)
\(g(4)-(g(3))^3=5\)
39.
Evaluate \(2g(1)-3f(5)\text{.}\)
\(2g(1)-3f(5)=-3\)
40.
Evaluate \(\frac{1}{2}f(10)-3f(1)\text{.}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}f(5)-3f(1)=2\)
41.
Evaluate \((f(-2))^2-g(2)-\frac{1}{3}g(5)\text{.}\)
\((f(-2))^2-g(2)-\frac{1}{3}g(5)=0\)
Exercise Group.
Suppose \(g(x)\) is given in the graph below and \(h(x)\) is given in the table below:
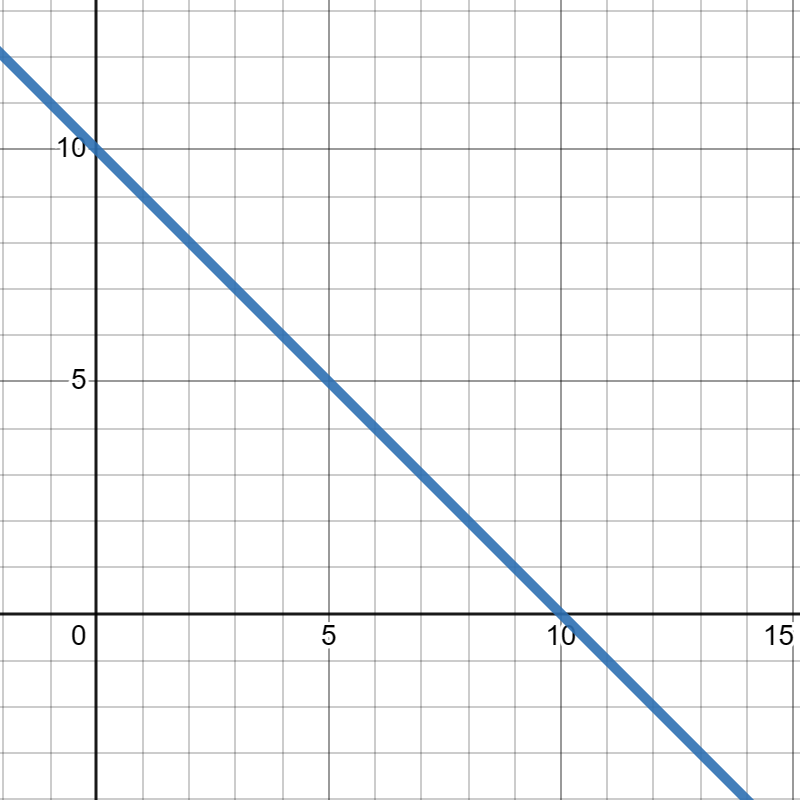
| x | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
| h(x) | 2 | 3 | 9 | 1 | 4 |
42.
Evaluate \(4h(2)-g(0)+3\text{.}\)
\(4h(2)-g(0)+3=5\)
43.
Evaluate \(g(4)-\frac{1}{2}(h(6))^3\text{.}\)
\(g(4)-\frac{1}{2}(h(6))^3=5.5\)
44.
Evaluate \(2g(1)+4h(8)\text{.}\)
\(2g(1)+4h(8)=34\)
45.
Evaluate \(\frac{1}{2}g(10)-3h(0)\text{.}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}g(10)-3h(0)=-2\)
46.
Evaluate \((h(4))^2-6g(2)-\frac{1}{3}g(1)\text{.}\)
\((h(4))^2-6g(2)-\frac{1}{3}g(1)=30\)
Exercise Group.
Suppose \(f(x)\) is given in the table below and \(g(x)=\frac{1}{2}x+2\text{:}\)
| \(x\) | \(f(x)\) |
| \(0\) | \(2\) |
| \(1\) | \(4\) |
| \(2\) | \(6\) |
| \(3\) | \(8\) |
| \(4\) | \(10\) |
47.
Evaluate \(3f(2)-g(2)+3\text{.}\)
\(3f(2)-g(2)+3=18\)
48.
Evaluate \(g(10)-\frac{1}{4}(f(3))^2\text{.}\)
\(g(10)-\frac{1}{4}(f(3))^2=-9\)
49.
Evaluate \(3g(1)+4f(4)\text{.}\)
\(3g(1)+4f(4)=47.5\)
50.
Evaluate \(\frac{1}{5}g(6)-3f(0)\text{.}\)
\(\frac{1}{5}g(6)-3f(0)=-5\)
51.
Evaluate \((f(1))^2-2g(2)-\frac{1}{3}g(-4)\text{.}\)
\((f(1))^2-2g(2)-\frac{1}{3}g(-4)=10\)
Exercise Group.
Suppose \(f(x)= 4x-8\text{.}\)
Exercise Group.
Suppose \(g(x)\) is given in the graph below.
Exercise Group.
Suppose \(f(x)\) is given in the table below.
| \(x\) | \(f(x)\) |
| \(1\) | \(3\) |
| \(2\) | \(6\) |
| \(3\) | \(9\) |
| \(4\) | \(12\) |
| \(5\) | \(15\) |
Exercise Group.
Suppose \(g(x)\) is given in the graph below.